Operational Procedures
Types of Nozzle
Slide /
Types of Nozzle
The type and quality of the nozzle can have a big impact on the production and operational outputs of the abrasive blast cleaning units.
Two types of nozzle design have existed in the industry:
- Straight bore nozzles
- Venturi style nozzle
This training unit will look at both of these types of nozzles.
Straight Bore Nozzle
This nozzle is sometimes referred to as a conventional style nozzle.
- At pressures of 100psi (7bar), the velocity of the abrasive leaving this type of nozzle is approximately 200 miles per hour (89 m/s)
- The straight bore blast gives a full impact in the centre section only
- This is illustrated in the photograph taken of a steel plate that has been previously coated
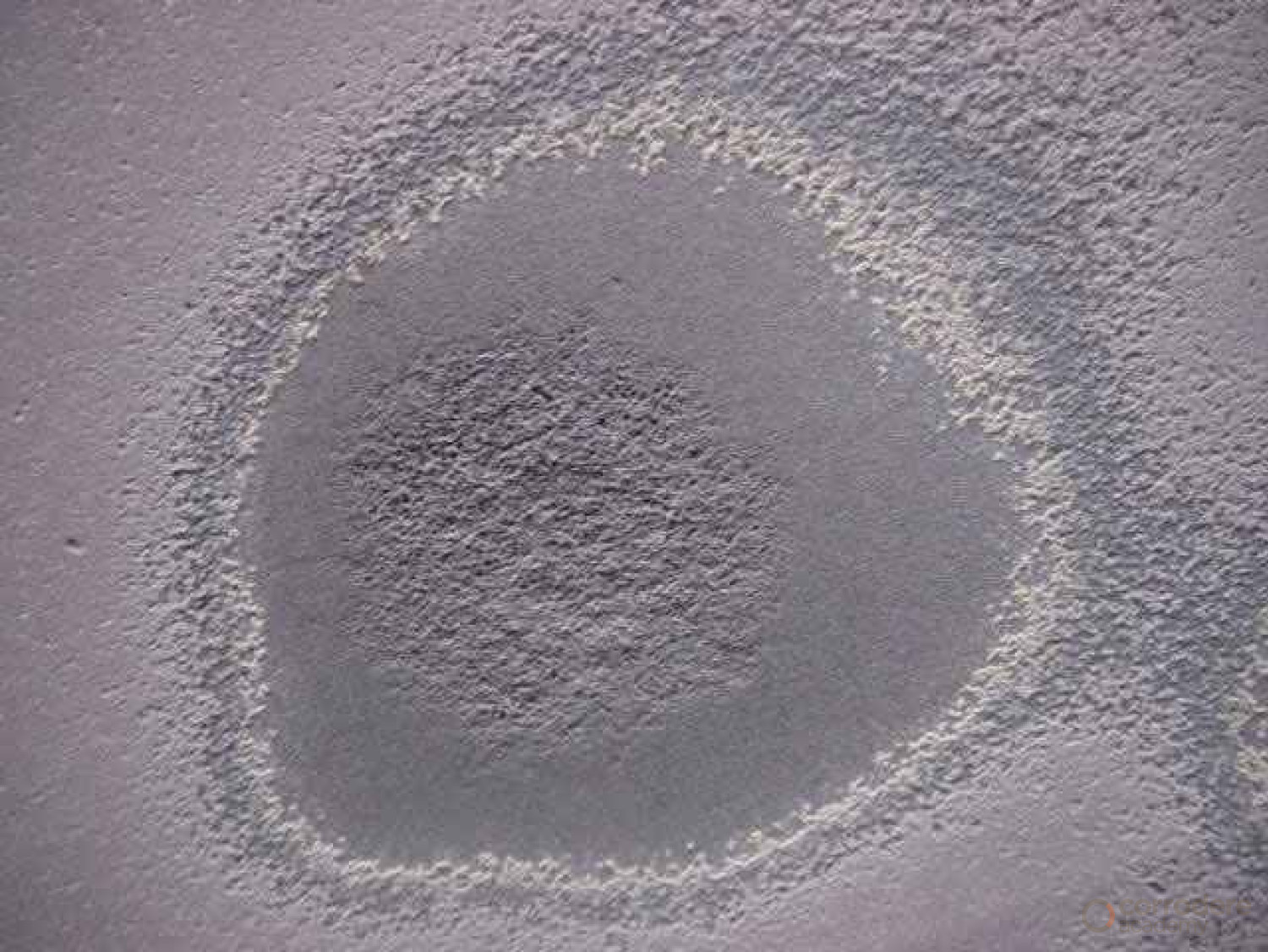
Straight Bore Nozzle
This illustration demonstrates an abrasive blast test with a straight bore nozzle held approximately 46 centimetres (18 inches) away from the surface.
- The full impact is approximately 12.5 centimetres which is under 5 inches
- There is a full and partial impact
- The partial impact will require additional blast cleaning to remove all the coating, taking additional time and cost
Venturi Shaped Nozzle
In the early 1960s venturi shaped nozzles were developed.
- This design allowed a more uniform impact over the entire pattern
- These nozzles made a big impact on the abrasive blast cleaning industry and have become very popular and are used extensively in the surface preparation industry
Venturi Nozzle
This illustration demonstrates an abrasive blast test using a venturi nozzle held approximately 46 centimetres (18 inches) from the surface.
- The full impact is 15 centimetres or nearly 6 inches
- There is no partial impact with the venturi nozzle, only full impact. The full impact is more effective and efficient
- This illustration demonstrates how this type of nozzle is now extensively used for abrasive blast cleaning, especially on large surfaces
Venturi Shape Nozzles
The venturi shape nozzle has a large entrance mouth.
- The large entrance mouth allows better flow of abrasive through the nozzle by eliminating turbulence and friction found with straight bore nozzles
- The venturi style nozzle is the main nozzle used for industrial works and large type contracts where large volume blast cleaning is conducted
Nozzle Types
This image illustrates the difference between the straight bore nozzle and the venturi shaped nozzle.
- The venturi shaped nozzle is more efficient than the straight-bore nozzle
- An operator can check the type of nozzle before it is fitted simply by looking down the funnel
Nozzle Comparison Chart
This comparison chart illustrates the differences between cast iron, ceramic and tungsten carbide nozzles.
- The life expectancy between nozzle types varies tremendously
- It is always worth reviewing the life expectancy of the nozzle before selecting
- Long life nozzles will be initially more expensive but maybe more economical over time
Boron Alloy Nozzle
A relatively inexpensive nozzle.
- This nozzle is used extensively for site work but is prone to mechanical damage
- Life expectancy is 40-60 hours, depending upon the type of abrasive used
- Typically these nozzles are used a lot longer than recommended. Additional abrasives are then used
- The nozzle is generally held in place with a lightweight nozzle retaining nut and nozzle gasket
Abrasive Blast Cleaning on Site
This video demonstrates the use of abrasive blast cleaning on a site structure.
- Boron alloy nozzles are generally used with expendable abrasives
- The environment dictates that these nozzles get a lot of abuse and have to be changed regularly due to damage from being dropped onto a steel surface etc.
- Spare nozzles should always be available
Spot Blasting
When spot blasting or blasting at low pressures, you have to select the correct nozzle to suit the requirements of the specific task.
- Smaller nozzles, which are manufactured for smaller hoses, are ideal for spot blasting and repairs
- Bigger nozzles and hoses will not give the operator the same level of control
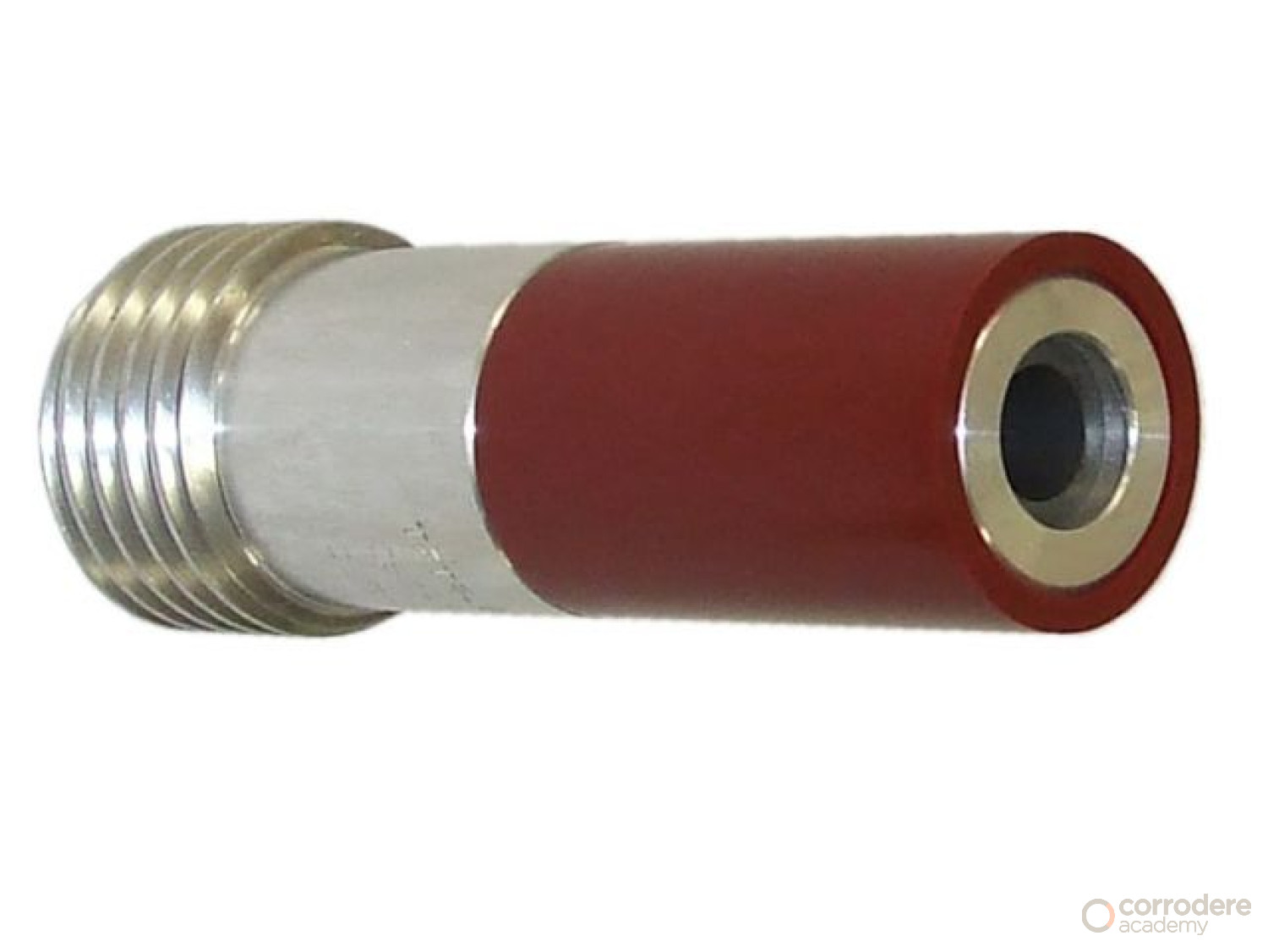
Boron Alloy Nozzle
This illustrates a boron alloy nozzle held in place on the blast hose with an aluminium retaining nut into a gasket.
- This retaining mechanism is safer than a nozzle held with a tightening clip, which is often found on site equipment
- This set up is generally found in factory abrasive blast chambers where a better maintenance program is generally in place
Less abuse is also found in factory blast equipment compared to site blast cleaning equipment.
Silicone Carbide (lined nozzle)
A silicone carbide nozzle is a very long life type nozzle with an expected life of up to 2,000 hours.
The nozzle is lightweight and will generally outperform most nozzles.
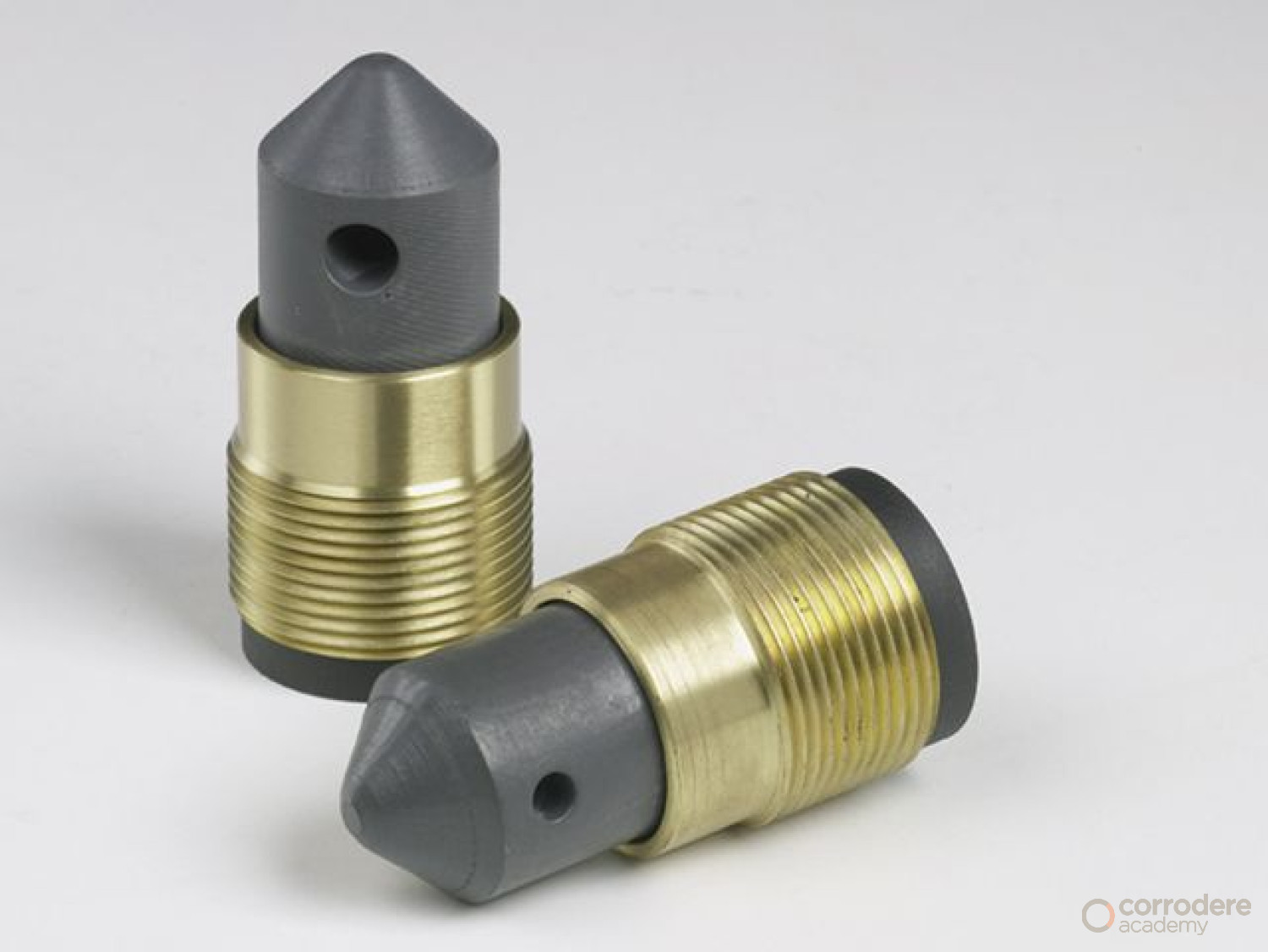
Boron Carbide Nozzle (illustrated)
Extremely abrasive resistant.
Generally very expensive but can last a long time if looked after and not abused.
Special Nozzles
There are specific applications where very tough abrasives such as aluminium oxide and silicon carbide abrasives are required.
- Traditional nozzles would wear away fairly rapidly with these types of abrasives
- Special nozzles with a 'cyclone' liner are available, which can handle these types of abrasives
- These nozzles are also the venturi type to assist with the full surface impact, as discussed earlier
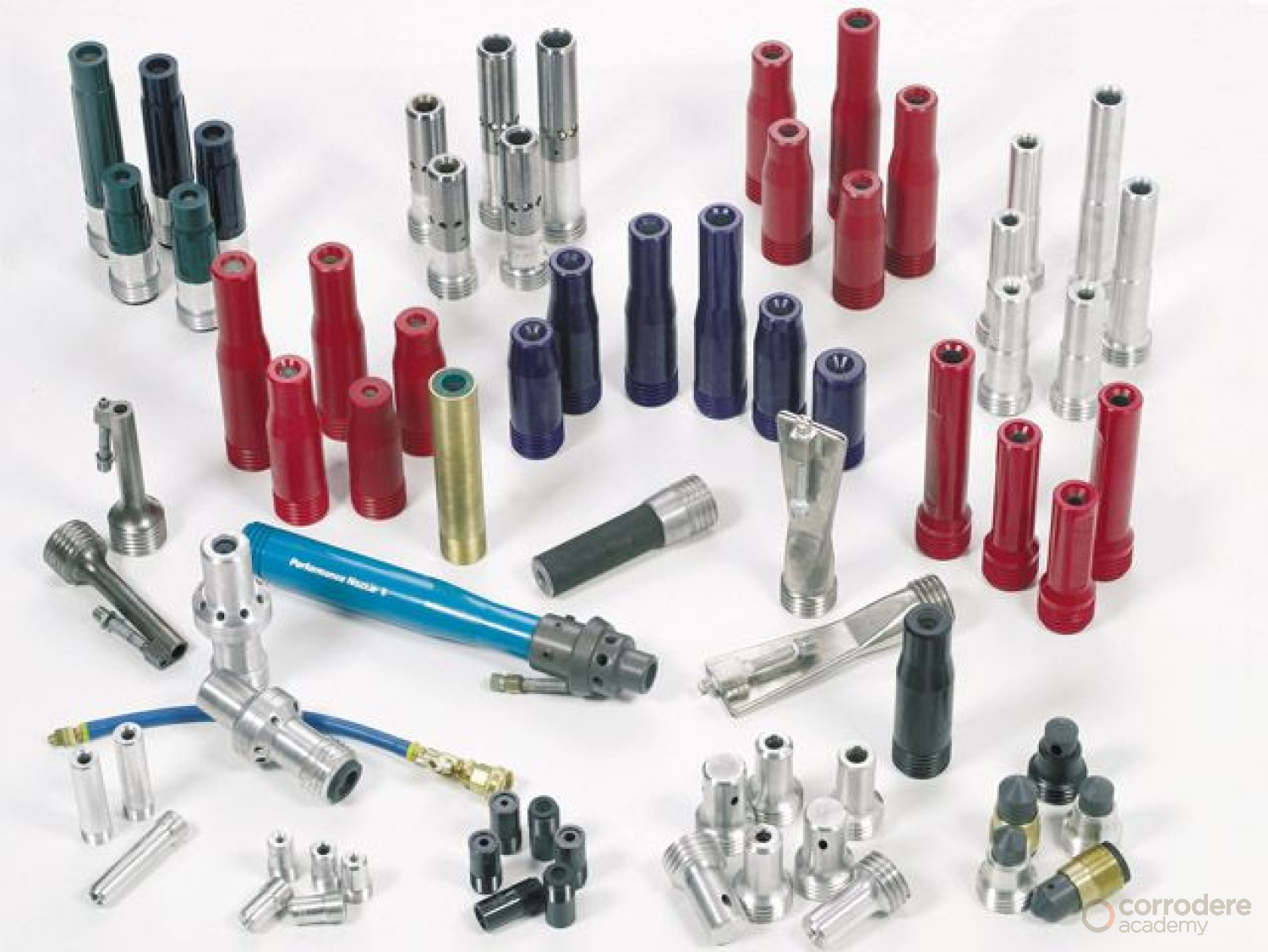
Nozzle Selection
This illustration demonstrates the various types of nozzles available to the abrasive blast cleaning operative.
- The size and type of nozzle will vary depending on the task to be performed
- Nozzles have a big impact on the efficiency of abrasive blast cleaning, so it is essential to review the type of nozzle to be purchased and used
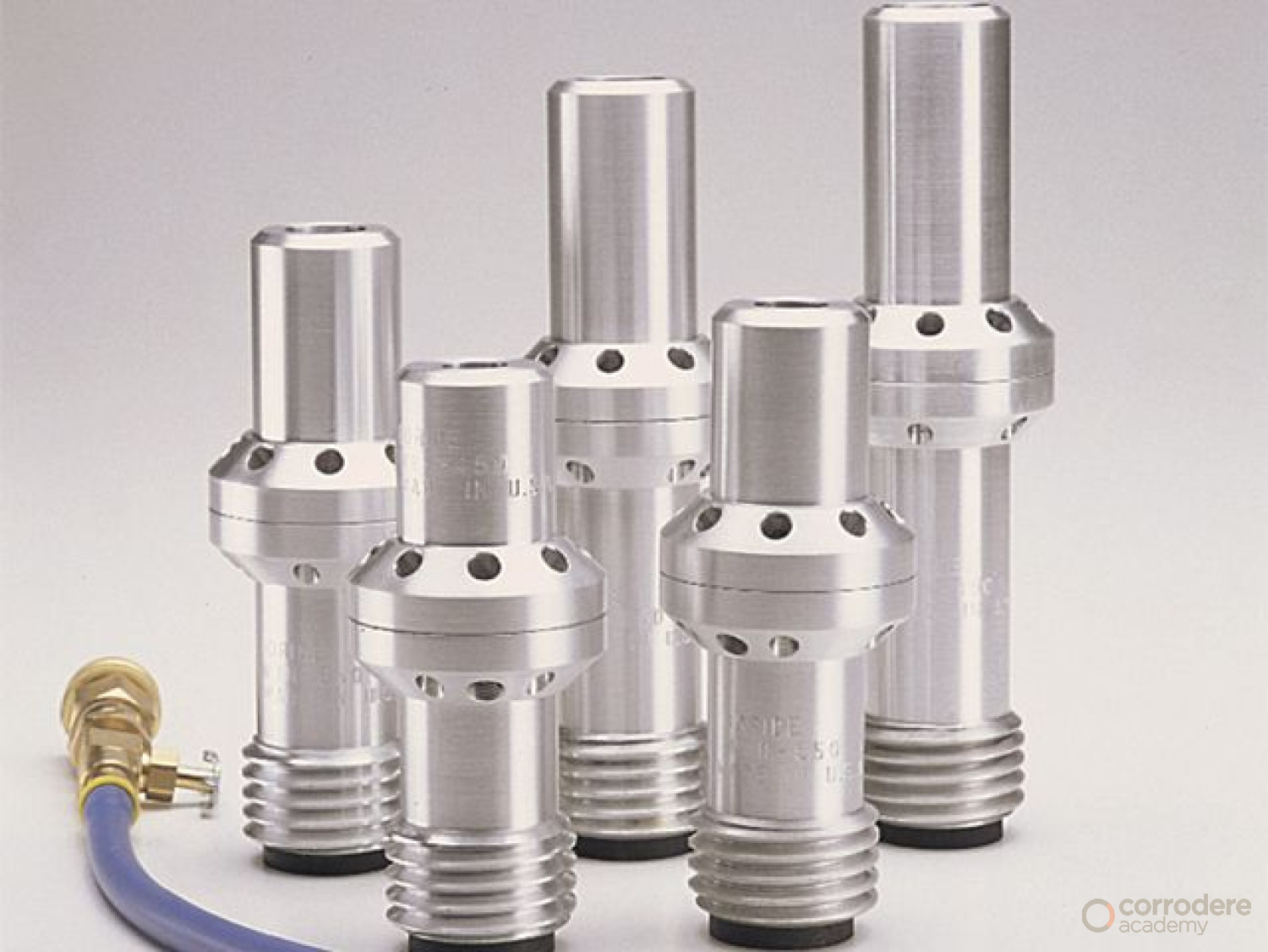
Specialist Nozzles
Specialised nozzles are also available.
- These are generally made from the same materials as venturi nozzles. Specialised nozzles are available in short and angled sizes
- Other specialised nozzles are available for wet abrasive blast cleaning and other tasks
- This picture demonstrates the various type of nozzles used with wet abrasive blast cleaning equipment
Wet Abrasive Blast Cleaning
This video demonstrates wet abrasive blast cleaning.
- Various non-metallic abrasives can be used with wet abrasive blast cleaning
- Specialised purpose-made wet abrasive blast nozzles are used for this process
- Water is mixed with the abrasive in some of these nozzles
Wear and Tear
Nozzles supplied by reputable suppliers should be well-designed with precise inlet, orifice and outlet dimensions.
- Wear and tear are inevitable in all nozzles. By virtue of the process, nozzles will have to be replaced
- A nozzle inspection gauge or visual inspection can be conducted to assess the wear and tear of the nozzle
- Visual inspection of the nozzle is easy to conduct
Nozzle Inspection
This animation demonstrates the use of a Pressure Blast Analyzer Gauge for checking a nozzle for wear and tear.
- The inspection is a quick and easy test that should be conducted prior to the commencement of the work
- Worn nozzles are not effective and should not be used
- Always have spare nozzles available
Wear and Tear
A worn nozzle will consume more air, and this can lead to a drop in nozzle pressure, which in turn reduces efficiency.
The larger the orifice:
- Increased abrasive use
- Greater air consumption
This adds up to more costs.
If you manage the nozzles correctly, you will save money!
Air Consumption Table
This table illustrates the air consumption represented in cubic feet per minute of blast cleaning nozzles at various pressures.
- The use of such charts is helpful for calculating the pressure requirements for different size nozzles
- The nozzle number corresponds with the diameter of the nozzle
- A No.3 nozzle has a 3/16" nozzle orifice
- A No.5 nozzle has a 5/16" nozzle orifice
Inspection of Nozzle
The user should always ensure the following:
- That the nozzle gasket is not worn
- An externally fitted nozzle holder is used
- The right size nozzle is used
- The nozzle pressure is correct. This can be checked by a hypodermic needle
Nozzle Pressure Testing Kit
A nozzle test kit contains the pressure gauge and hypodermic needles.
- The hypodermic needle is attached to the pressure gauge and inserted into the blast hose just behind the nozzle
- This test will give an instant pressure reading
- The same test can be done near the compressor or mid-length to establish any pressure drop
Pressure in the Blast Hose
This animation illustrates the use of a hypodermic needle gauge to check the pressure in the abrasive blast hose.
- The needle must be placed on an angle to follow the flow of air and abrasive
- This is a simple test and worthwhile conducting as it gives an immediate indication of the pressures
Curved Nozzle
It is possible to attach 40-degree curved nozzles to blast clean difficult areas.
- These nozzles are attached to a steel jacket and thread and are boron carbide lined
Angle Nozzles
45-degree angle nozzles have been used with success on structures where traditional (and curved) nozzles can not reach.
- These nozzles are lined with tungsten carbide. However, due to the acute angle, the nozzle will wear away considerably faster than traditional tungsten carbide lined nozzles during use
- The blast hose type and diameter have to be correctly set up for this type of blast nozzle
Multi-Nozzle Wand
When it is essential to abrasive blast clean extremely tight locations, as illustrated, a special 'wand' type nozzle with double or triple orifice nozzles is available.
- The nozzle can use most abrasives and only requires a ¾" (19mm) clearance
- The process requires adaption for the blast hose and is relatively slow in comparison to traditional blast cleaning methods
Summary
This training unit reviewed the various types of blast cleaning nozzles used for abrasive blast cleaning.
On the traditional nozzles, we have reviewed the straight bore and venturi types and the advantages of the latter.
We have discussed the various types of 'new' nozzles that are extremely hard wearing and used for tough abrasives.
We also discussed the nozzles that can be used for awkward locations and tight spaces.
Nozzle wear and tear were reviewed, along with blast hose pressure testing.

























-1.jpg?w=1500&h=1126&fit=crop&mark=logo.png&markw=200&markpos=bottom-right&markpad=20&markalpha=35&s=d583cf604e013be3d466520d687f464a)
-1.jpg?w=750&h=563&fit=crop&mark=logo.png&markw=200&markpos=bottom-right&markpad=20&markalpha=35&s=af5aaa1e2ae21a7c4dcdb9ffdebf8444)















